반응형
Refrence : David Harris, Sarah Harris - Digital Design and Computer Architecture
Topics
- Memory System Performance Analysis
- Caches
- Virtual Memory
- Memory-Mapped IO
8.1 Introduction
컴퓨터의 성능은 다음 요소에 의해 결정된다.
- Processor performance
- Memory system performance

⇒ 하지만, 기술이 발전하면서 single core 성능을 높이는데 한계에 달았고, 이제memory system의 성능을 높이는 것이 중요하다. ⇒ 빠르고, 싸며, 용량이 큰 이상적인 메모리를 만들어야 하지만, 세가지 요소를 모두 충족시킬 수 없어 2가지만을 충족시키는 여러 메모리 hierarchy를 둔다.
Memory Hierarchy

8.2 Memory System Performance Analysis
Locality
- Temporal Locality : data를 읽으면 해당 data를 곧 다시 읽을 확률이 높다 ⇒ 높은 메모리 계층에 잠시 저장해 둔다. (caching)
- Spatial Locality : data를 읽으면 그 주변 data도 읽을 확률이 높다. ⇒ 그 주변까지 함께 읽는다.
Memory Performance
- Hit: request 왔을 때, 해당 메모리 계층에서 그 data가 있는 경우
- Miss : Hit의 반대, data가 없을 때.

- Average memory access time (AMAT)
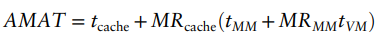
Example


8.3 Cache
- 가장 높은 계층의 메모리로 빠르며 대부분의 accessed data를 들고있다.
cache를 설계한다고 했을 때 다음 3가지 질문이 있을 것이다.
- What data is held in the cache?
- How is data found?
- What data is replaced?
하나씩 살펴보자.
(1) What data is held in the cache?
- 미래에 사용될 것이라 예상되는 data를 담는다.
- 하지만 미래를 예측할 순 없기에 temporal and spatial locality를 사용한다.
Cache Terminology
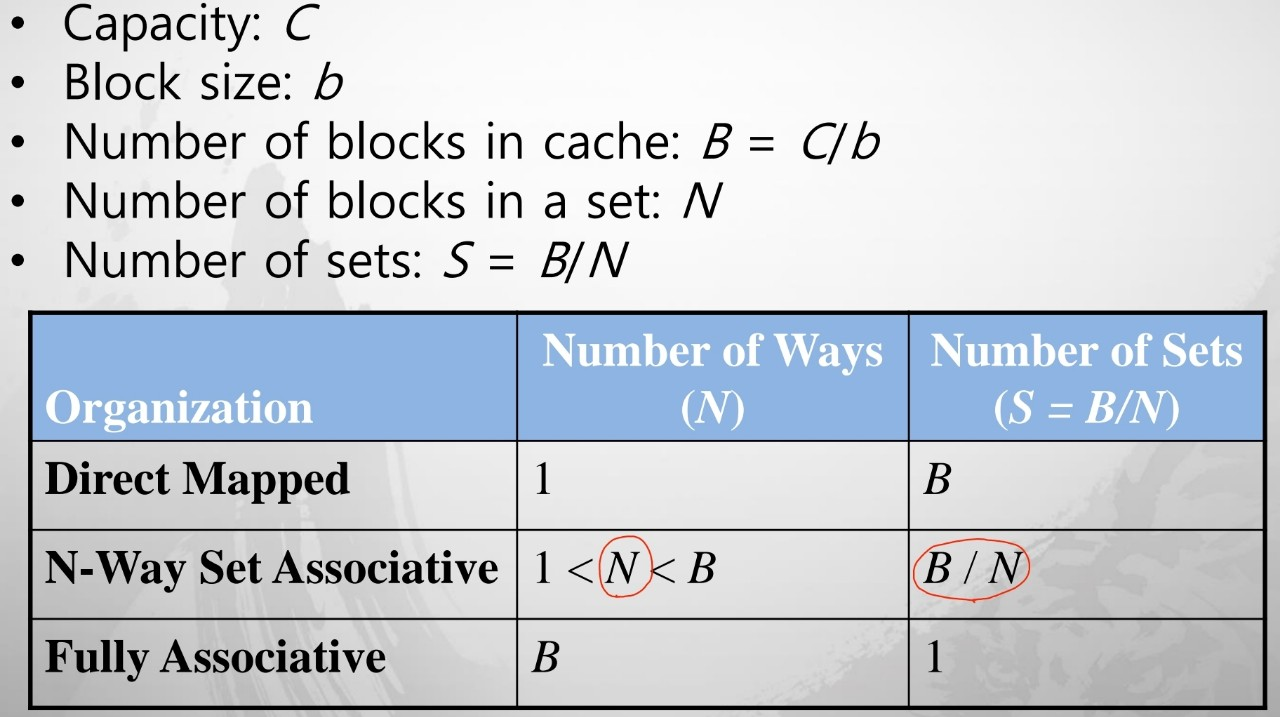
- Capacity (C) : cache 내 data byte 개수
- Block size (b) : cache로 1번 접근할 수 있는 bytes
- Number of blocks (B= c/b) : cache 내 block 개수
- Degree of associativity (N) : set 내 block 개수
- Number of sets (S= B/N) : 각 memory 주소는 하나의 cache set과 매핑
(2) How is data found?
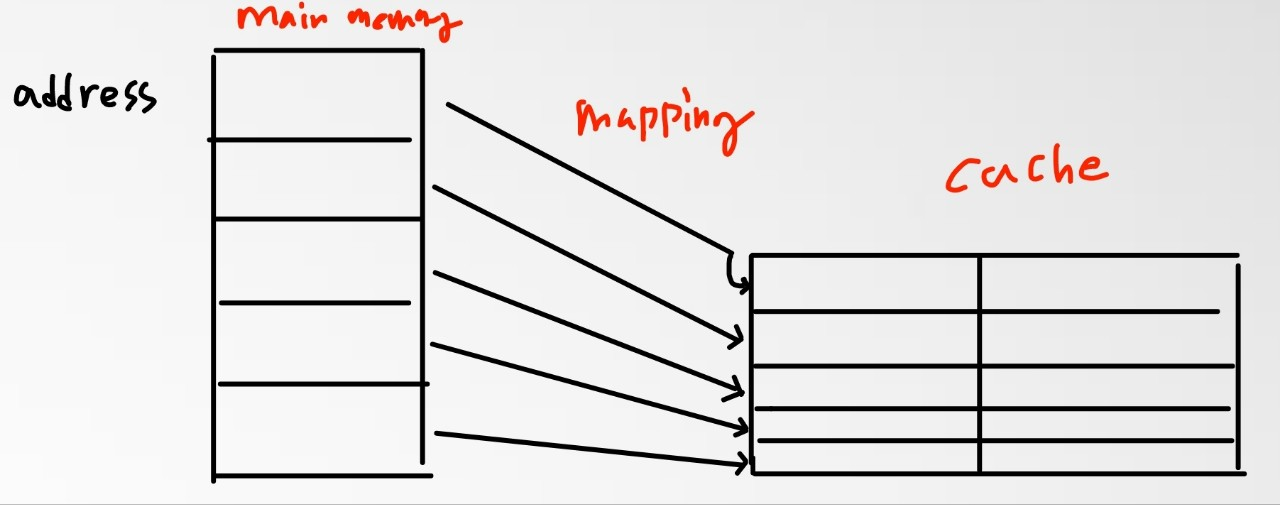
- cache는 set 들로 구성된다.
- 각 memory 주소는 하나의 set과 mapping
- set 내에 block을 몇개 넣는지에 따라 분류한다.
- Direct mapped: 1 block per set
- N-way set associative: N block per set
- Fully associative: 하나의 set에 cache의 모든 block
Direct Mapped Cache
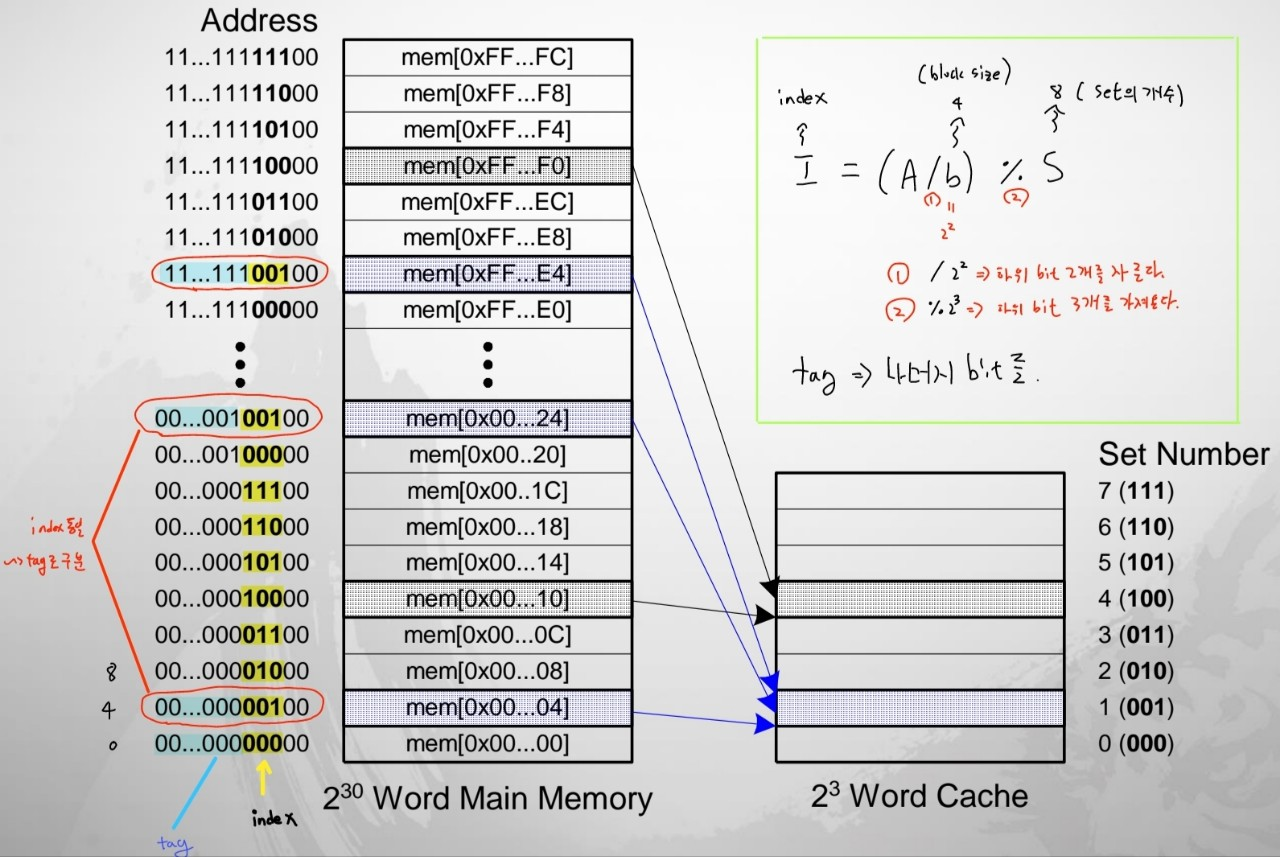
- index: I = (A/b) % S
- tag : 나머지 bit들
⇒ 이 두가지로 Set과 memory 주소를 연결한다.
Direct Mapped Cache Hardware
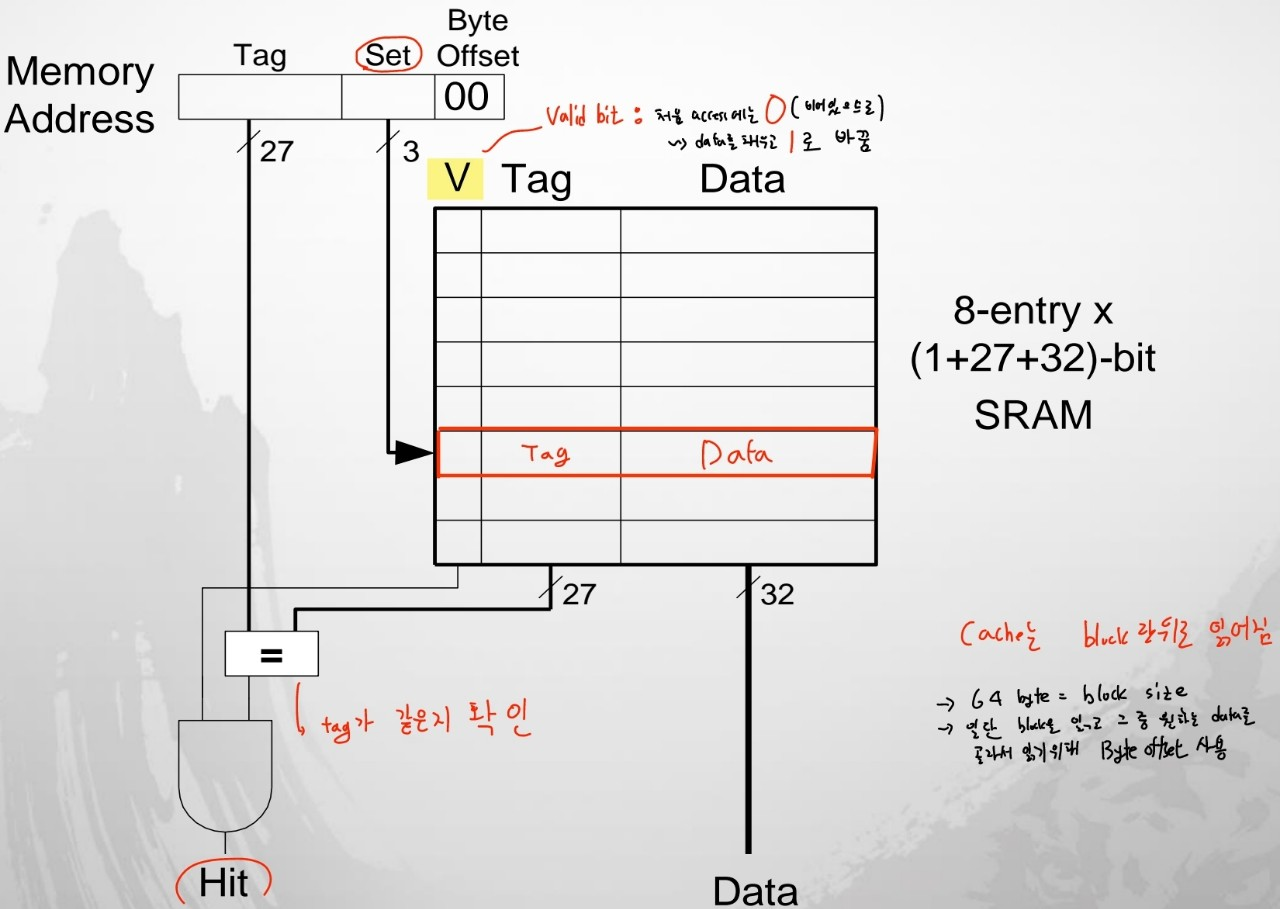
- valid bit: 0으로 초기화, Data를 채우고 1로 바꾼다.
- tag가 같은지 확인하고 data를 넣는다.
Example1


색을 따라서 cache에 어떻게 data가 들어가는지 표시하였다.
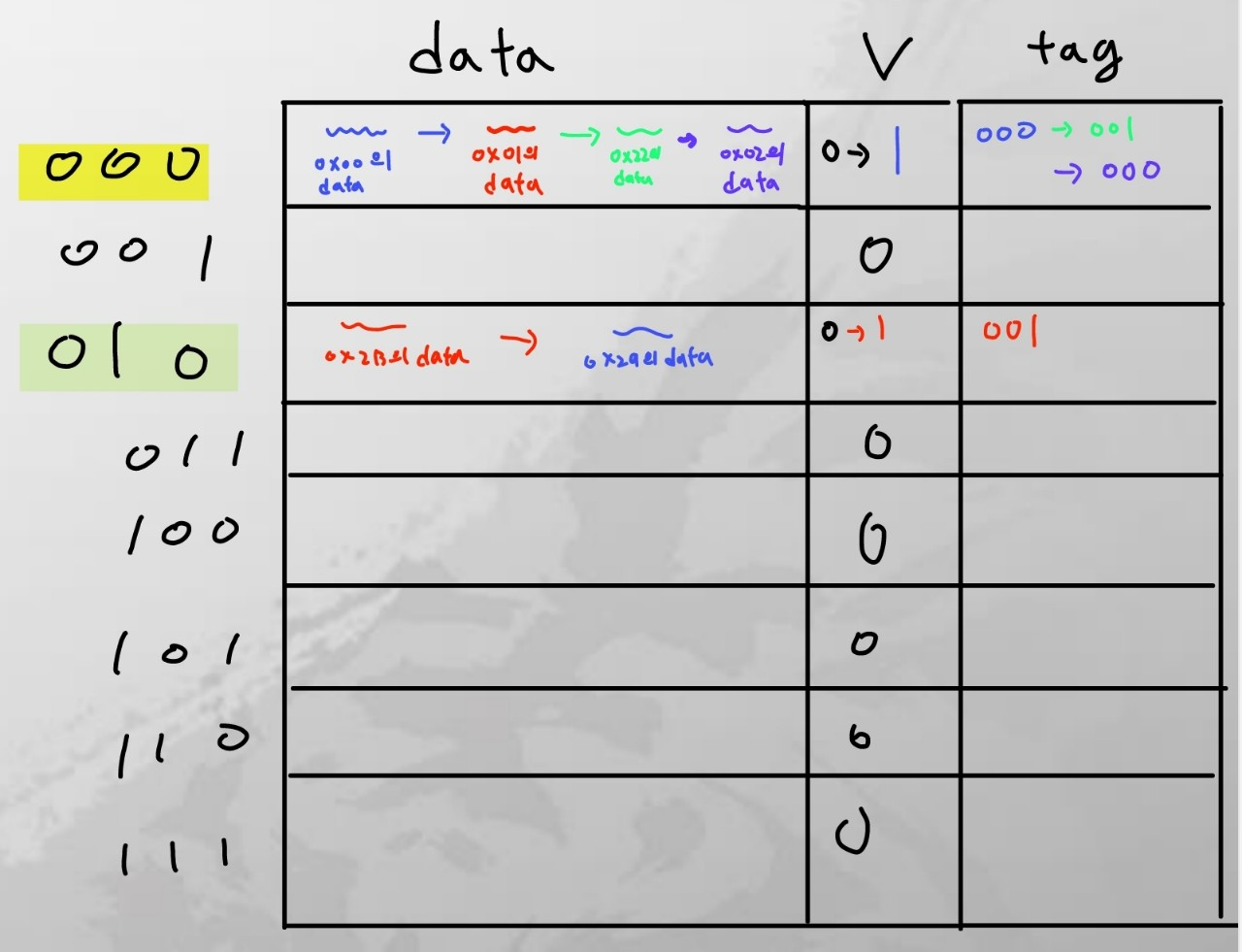
- 한번 접근하면, Miss가 나더라도 data와 tag를 저장하여 다음에 접근할 때 같은 값을 찾는다면 Hit이 날 수 있도록 한다.
Example2
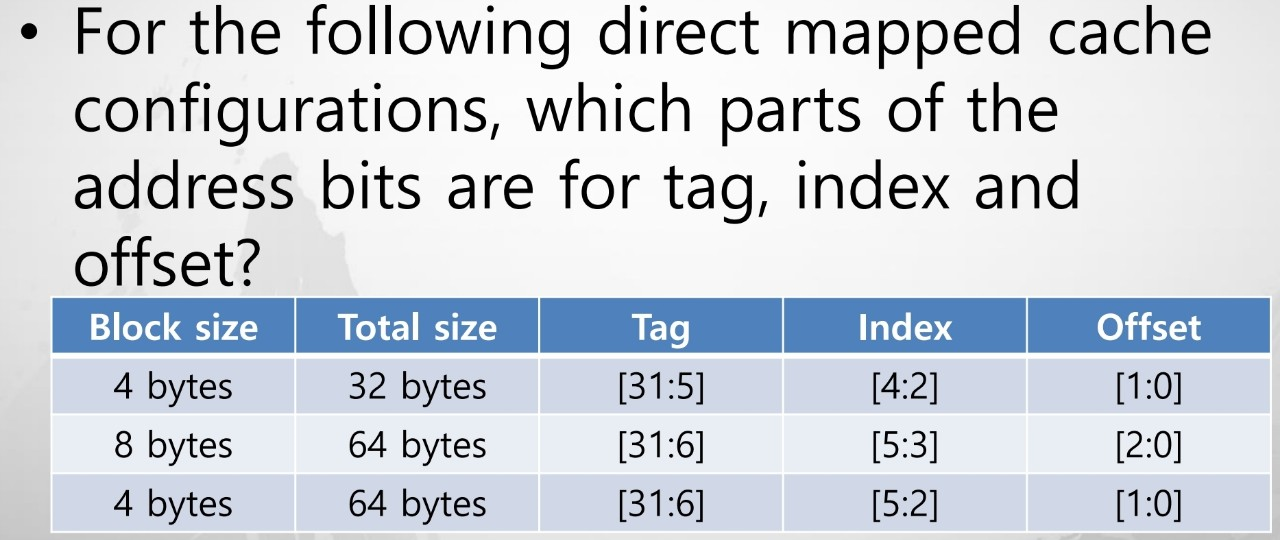
Direct Mapped Cache Performance
(1) Compulsory Misses

- 첫 loop에서만 Miss가 3번이 나고, 이후 모두 Hit가 뜬다. (compulsory[cold] miss)
(2) Conflict Misses
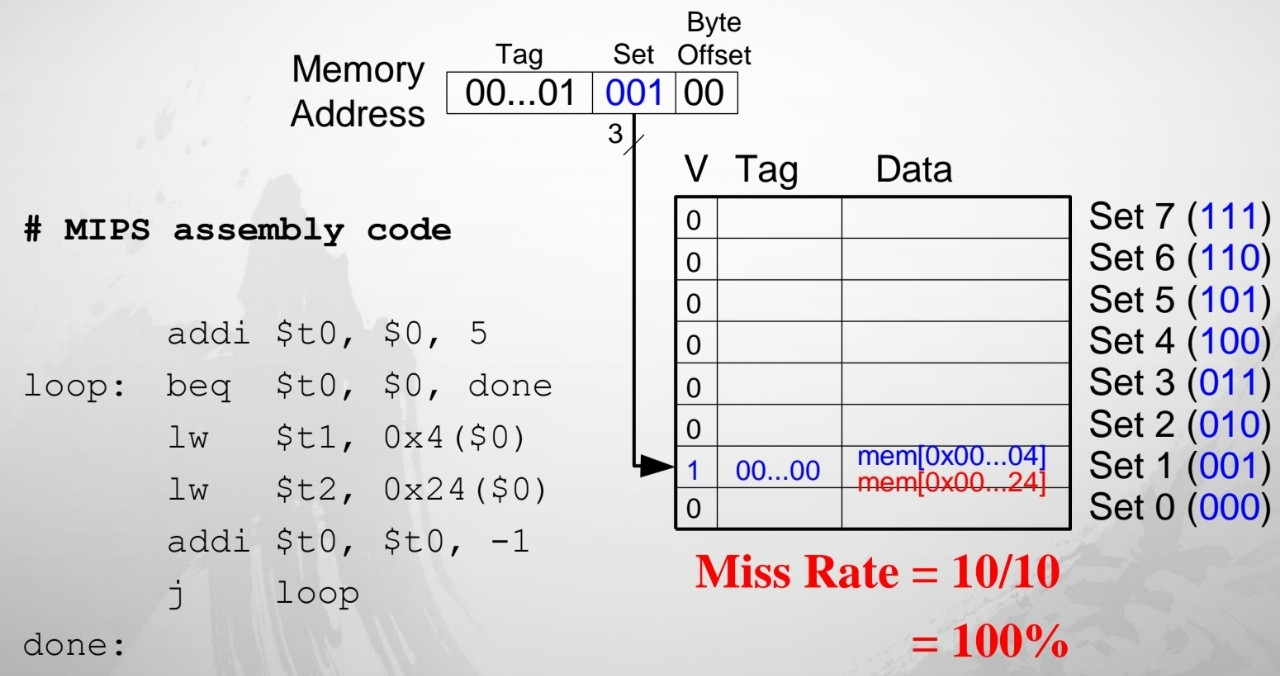
- Miss이후 0x4 data를 넣는다. → 0x24랑 안 맞으니 또 Miss, 0x24 data를 넣음 → 이후 무한 반복하여 100% Miss만 나오는 상황
N-Way Set Associative Cache
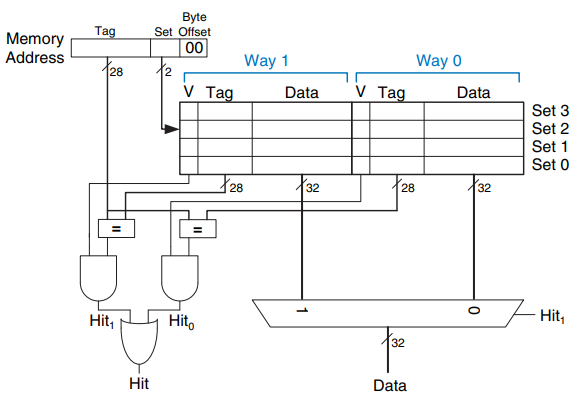
- 하나의 set에 여러 block이 들어있는 경우
- conflicy miss를 방지할 수 있다.
N-Way Set Associative Performance
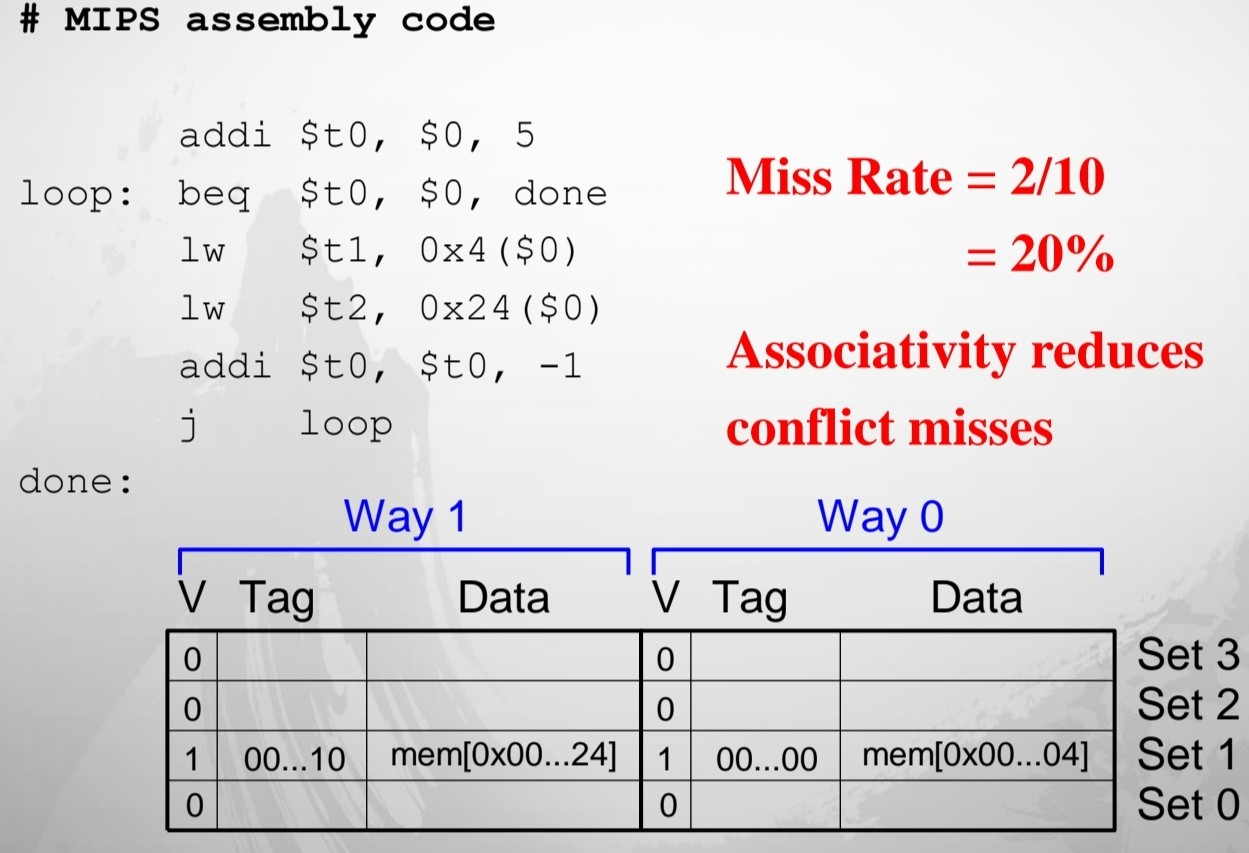
- 처음에 cold miss만 있고, 이후에는 conflict miss는 더 이상 발생하지 않음
Fully Associative Cache
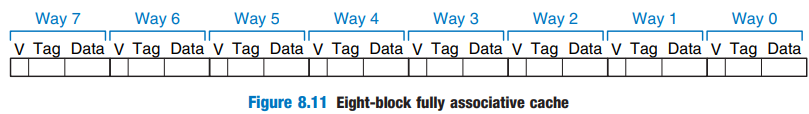
- conflict miss를 거의 일으키지 않지만, 비용이 비싸다.
위와 비슷한 문제를 풀어보면 아래와 같다.
Example1

Example2

Block size를 증가시키는 경우
Cache with Larger Block Size
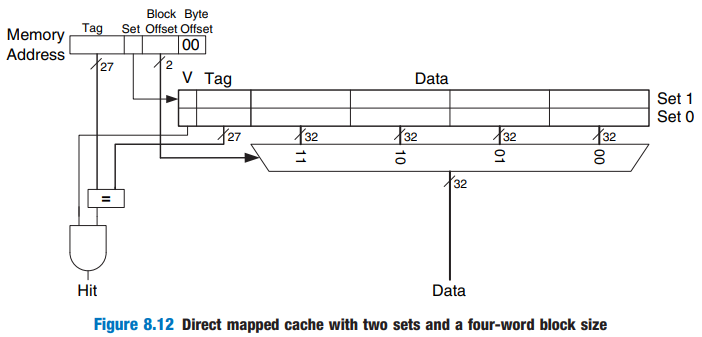
- b = 4 words, block size
- C = 8 words
- Direct mapped
- Number of blocks, B - 2 (C/b = 8/4 =2)
Direct Mapped Cache Performance
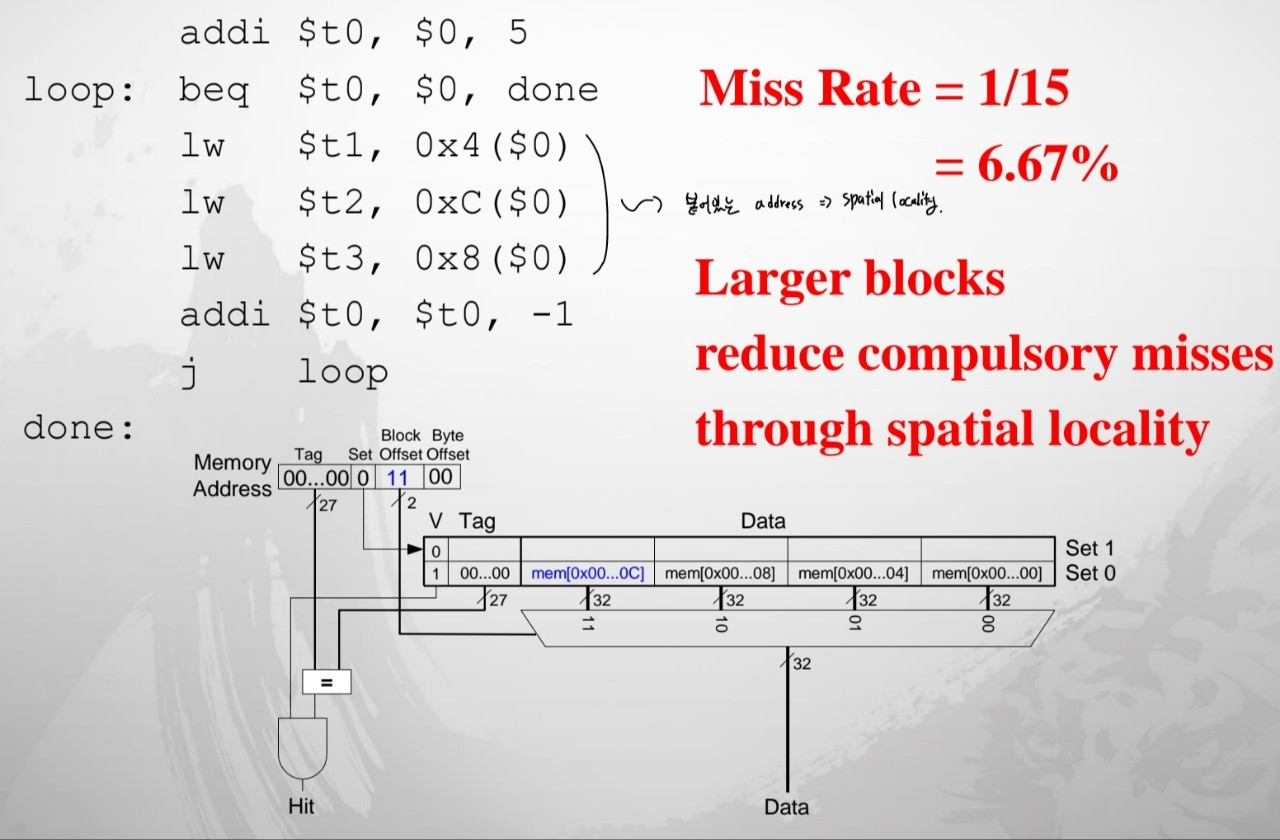
Capacity Misses
- cache는 너무 작기 때문에 어떤 작업에 필요한 모든 데이터를 다 담을 수 없다.
- 만약 cache가 꽉 찬다면, 기존에 있던 data를 없애는데, 만약 방금 없앤 data를 누군가 access한다면 Cache miss가 발생한다.
- 이를 최대한 줄이기 위해 다양한 정책을 정해서 수행한다.
Types of Misses
- Compulsory: data에 처음 접근
- Capacity: cache 용량이 작음
- Conflict: data들이 cache 상 같은 위치에 매핑
Miss penalty
- cache에 없어서 낮은 계층의 메모리로 해당 block을 가져오는 시간
LRU Replacement
- 가장 최근에 사용한 data는 keep하고,
- 오래된 것부터 replace한다.

Cache Summary
(1) What data is held in the cache?
- 최근에 사용한 data - temporal locality
- 근처에 있는 data - spatial locality
(2) How is data found?
- Set, block이 data의 주소를 결정
- associative cache에서는 data가 다양한 way에 저장 가능
(3) What data is replaced?
- LRU 정책
Multilevel Caches
- cache 자체에 hierarchy를 두어 더욱 최적화
반응형
'Computer Science > Computer Architecture' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터 구조] Ch8. Memory and I/O Systems(2) Virtual memory (0) | 2022.12.07 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터 구조] Ch7. Microarchitecture (0) | 2022.11.19 |
| [컴퓨터 구조] Ch6. Architecture (3) - Addressing Mode, Odds & Ends (0) | 2022.10.09 |
| [컴퓨터 구조] Ch6. Architecture (2) - Programming (0) | 2022.10.09 |
| [컴퓨터 구조] Ch6. Architecture (1) - Assembly Language, Machine Language (1) | 2022.10.08 |
![[컴퓨터 구조] Ch8. Memory and I/O Systems(1) - Cache](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FnpNF7%2FbtrS6SHOaRP%2FGFqTdvT4PSaByPAq6bBZ9K%2Fimg.png)