반응형
Reference
1. Database System Concepts-Abraham Silberschatz, Henry Korth, S. Sudarshan
2. Database System class by Professor Yon Dohn Chung, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Korea University
중요한 내용 위주로 요약 & 정리하였습니다.
목차
- Overview
- Mesasures of Query Cost
- Selection Operation
- Sorting
- Join Operation
- Other Operations
- Evaluation of Expressions
1. Overview
Basic Steps in Query Processing
- Parsing and translation : query → relational algebra 변환
- Optimization
- Evaluation : query-evaluation plan을 실행하여 결과 반환

- relational algebra expression은 다수의 equivalent expression이 있을 수 있다.
- 각 relational algebra operation은 다양한 알고리즘으로 계산된다.
- evaluation-plan : 구체적인 evaluation 전략
Query Optimization
- 모든 equivalent evaluation plan에서 비용이 가장 낮은 것을 선택
2. Measures of Query Cost
- response time : 쿼리에 응답하기 위한 총 경과 시간
- resource consumption : 총 자원 소비량
→ 이 장에서는 단순하게 CPU, 네트워크, 디스크 출력 비용을 고려하지 않는다.
Disk cost
- number of seeks * average-seek-cost (탐색 횟수 * 평균 탐색 비용)
- number of blocks read * average-block-read-cost (블록 읽기 수 * 평균 블록 읽기 비용)
- number of blocks written * average-block-write-cost (기록된 블록 수 * 평균 블록 쓰기 비용)
단순하게 “seek”와 “block transfer”만 고려

3. Selection Operation
- File scan
- Index scan - index를 사용하여 scan
(1) linear search
Cost estimate = br block transfers + 1 seek
- 만약 key attirbute에 대한 selection일 경우 cost = (br /2) block transfers + 1 seek
- binary search X → 먼저 정렬되어야 함, seek가 많아짐
index 사용한 selection
(2) Clustering index, equality on key
- clustering index → leaf node에서의 pointer 순서 == record search key 순서
- index tree의 height + 1 만큼 seek

(3) Clustering index, equality on nonkey
- b : matching되는 record를 포함한 block의 개수
- ex) 홍길동 100명 → seek는 1번으로 같지만, block transfer는 b번 만큼 수행
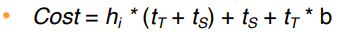
(4) Secondart index, equality on key/non-key
- search-key가 candidate key

- search-key가 candidate key 아님 → block transfer 뿐만 아니라 seek도 n번

Comparisons
- linear file scan
- using indices
(5) Clustering index, comparison
- 큰 값을 찾는 경우 : index 사용
- 작은 값을 찾는 경우 : sequentially scan

(6) Secondary index, comparison
- 큰 값을 찾는 경우 : index 사용
- 작은 값을 찾는 경우 : scan leaf pages of index

Conjunction
- and 조건 연결
- selectivity : 쿼리문에서 가져오는 비율 → 작을 수록 query 수행 시간이 좋다.
(7) Conjunctive selection using one index
- 여러 알고리즘 조합 중 가장 비용이 적게 드는 조합을 선택
(8) Conjunctive selection using composite index
- 사용 가능한 적절한 multiple-key index를 사용
(9) Conjunctive selection by intersection of identifiers
- 각 조건에 해당하는 인덱스를 사용하고, 그렇게 얻은 모든 record끼리 교집합을 구한다.
Disjunction
- or 조건 연결
(10) Disunctive selection by union of identifiers
- 각 조건에 해당하는 인덱스를 사용하고, 그렇게 얻은 모든 record끼리 합집합을 구한다.
- 사용 가능한 인덱스 없으면 linear scan 실시
(11) Negation
- not 조건
- linear scan 사용
(12) Bitmap index scan
- linear scan과 secondary index scan의 조합
- rocord id를 index scan하여 찾고, bitmap에 따라 bit 설정
- linear scan으로 bit가 1로 설정된 page만 가져옴
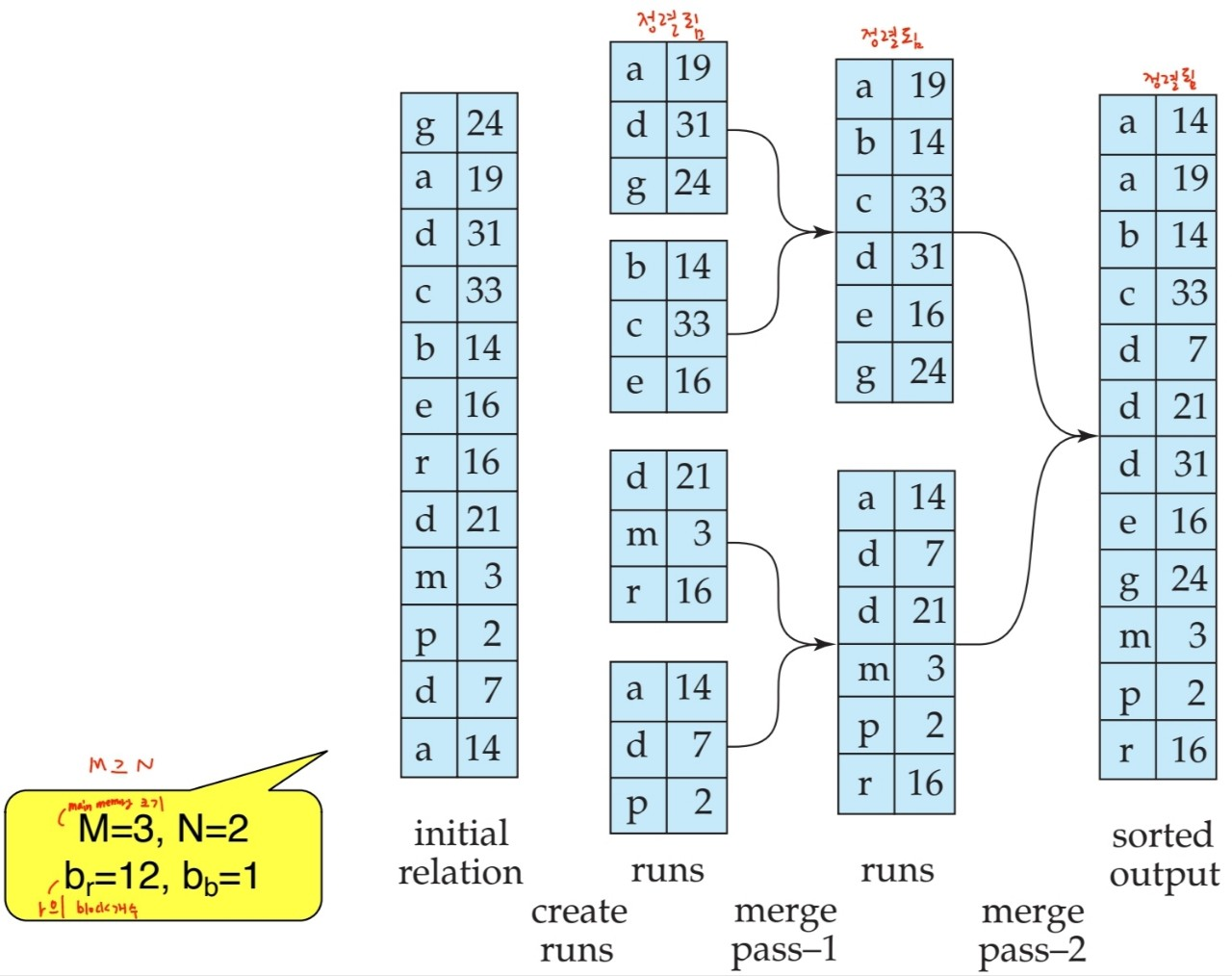
4. Sorting
- relation이 memory에 맞는다면, internal sorting 실시 - quick sort
- relation이 memory에 맞지 않는다면, external sort-merge 실시 - merger sort
external sort-merge
5. Join Operation
- Nested-loop join
- Block nested-loop join
- Indexed nested-loop join
- Merge-join
- Hash-join
(1) Nested-Loop join - 안 씀

- r : outer relation - loop 바깥
- s : inner relation - loop 안
- worst case : memory에 오직 한 block만 올라갈 수 있는 경우

- best case : memory에 모두 올라간 경우

⇒ inner relation을 작은 것으로 하면 더 효율적이다.
(2) Block Nested-Lop join - 상위 호환

- block을 올릴 때 여러 개의 block이 memory에 올라감 → 어차피 memory에 올라간 김에 함께 block을 읽는다.
- 4중 for문이지만 더 좋다.
- Nr → Br 로 줄일 수 있다.
- worst case

- best case

(3) Indexed Nested-Loop join
- index는 inner relation의 join attribute 사용
- index를 사용하여 outer relation의 각 tuple에 대해 join condition을 확인
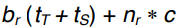
(4) Merge join
- 먼저 두 relation이 정렬되어야 함 (정렬 안되어있으면 정렬 시키고 진행)
- sorted relation들을 merge 한다
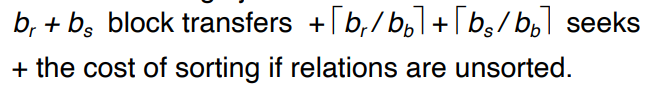
- hybrid merge-join : 한 relation만 정렬됨 → 다른 쪽은 secondary B+ tree index를 가질 경우 정렬된 relation과 B+ tree의 leaf entry끼리 merge를 실시한다.
(5) Hash join
- hash 함수를 사용하여 relation의 tuple을 분배
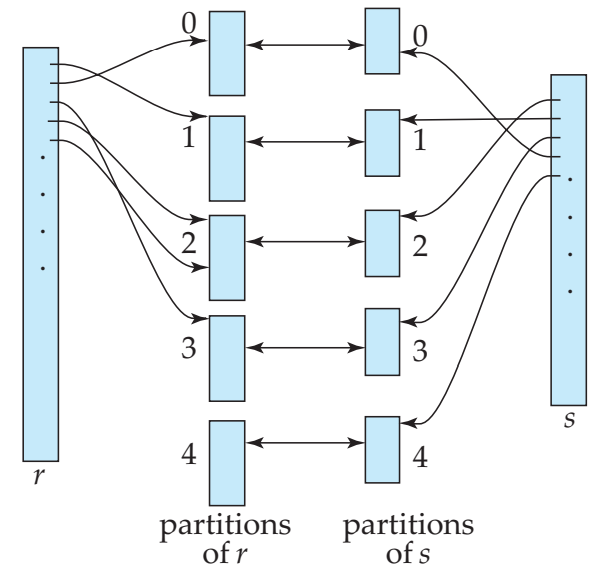
- 그림에서는 양쪽 모두 hashing했지만, 실제로는 하나만 hashing (build relation)하고 나머지가 sequential scan하면서 탐색 (prove relation)
- 조인될 두 테이블 중 하나를 해시 테이블로 선정하여 조인될 테이블의 조인 키 값을 해시 알고리즘으로 비교하여 매치되는 결과값을 얻는 방식
6. Other operations
- Outer join : 일반 join 알고리즘 확장
group by
Sorting과 hashing 사용 → 같은 group 묶기 → aggregate 함수 사용 가능
- distributive : sub-aggregation 으로 전체 aggregation을 구할 수 있는 경우
(count, min, max, sum) - ex) 예를 들어 각 부분 집합의 max는 전체에서의 max이다.
- algebraic : 조합해서 만들 수 있는 경우
(avg) - > sum과 count로 구현
- holistic : distributive의 반대.
(median) → 꼭 전체에 대해서만 계산 가능
7. Evaluation of Expressions
- Materialization : 이미 계산이 완료된 input으로 expression의 연산 결과를 disk에 저장
- Pipelining : parent operation에게 자신의 operation 결과가 나오자마자 전달
Materialized evaluation
- 가장 낮은 레벨부터 차례대로 처리해 나가는 방식, 결과를 임시 저장 공간에 저장하고 다음 단계에 전달
- 어떤 쿼리문이든 적용 가능
- 매 단계마다 메모리를 사용하기 때문에 비용이 높다
- double buffering으로 실행 시간을 줄인다.
Pipelining
- 한 연산의 실행이 끝나서 결과 값을 내기 전에, 다른 연산도 실행하는 방법 (동시에 계산)
- Materialization 보다 저렴하다 (따로 저장 x)
- 정렬, 해쉬 조인에는 적용 불가
demand driven(lazy driven)
- 현재 상태를 중심으로 다음 연산에 필요한 것을 요청
- pull
producer driven(eager driven)
- operator 사이에 버퍼가 존재하여 자식 operation이 buffer에 값을 넘겨주면 부모 operation이 가져와서 처리한다.
- push
Continuous querires
- 종료하기 전까지 계속 실행 중인 쿼리
- Data streams 처리 유용
- tumbling window → 겹치지 않은 구간을 반복
- sliding window → 겹침 허용
반응형
'Computer Science > Database' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [데이터베이스] Chapter 17. Transaction (0) | 2022.12.04 |
|---|---|
| [데이터베이스] Chapter 16. Query Optimization (0) | 2022.12.04 |
| [데이터베이스] Ch 14. Indexing(2) - ch24. 내용 추가 : Hashing, Spatio-temporal Indexing (0) | 2022.10.10 |
| [데이터베이스] Ch 14. Indexing(1) - Clustering, Non-clustering Index, B+ Tree Index Files (0) | 2022.10.10 |
| [데이터베이스] Chapter 13. Data Storage Structures (0) | 2022.10.08 |
![[데이터베이스] Chapter 15. Query Processing](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FbvNuEA%2FbtrOwxa7IeO%2FlHYXss0i4Ax8xhfgjZFx91%2Fimg.png)