반응형
Reference
1. Thomas Erl_ Zaigham Mahmood_ Ricardo Puttini - Cloud Computing_ Concepts, Technology & Architecture-Prentice Hall
2. Cloud Computing class by Professor Heonchang-Yu of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Korea University
중요한 내용 위주로 요약 & 정리했습니다.
목차
- Concept of cloud computing
- Basic Concepts and Terminology
- Goals and Benefits
- Risks and Challenges
1. Concept of Cloud Computing
- Cloud computing turns IT services into utilities without technological and legal barriers
- Cloud service provider와 consumer는 cloud service를 마치 utilities 처럼 거래
Defining a cloud computing
Cloud computing refers to both the applications delivered as services over the Internet and the hardware and system software in the datacenters that provide those services
- scalable(확장 가능)하고 elastic(탄력적)하게 IT 서비스를 인터넷을 통해서 서비스 형태로 제공하는 것
- pay-per-use strategy : 사용한 만큼만 돈을 지불한다.
- computing resorce를 언제 어디서나(ubiquitous) 필요할 때 사용할 수 있다.
- distributed computing (분산 컴퓨팅)의 한 종류이다.
XaaS : X-as-a-Service
- SaaS : Software as a Service
- IaaS : Infrastructure as a Service
- HaaS : Hardware as a Service
- DaaS : Database as a Service
2. Basic Concepts and Terminology
Cloud
- 확장 가능(scalable)하고 측정된(measured) IT 자원을 원격으로 프로비저닝할 목적으로 설계된 고유한 IT 환경
- 프로비저닝(provisioning) : 사용자의 요구에 맞게 시스템 자원을 할당, 배치, 배포해 두었다가 필요 시 시스템을 즉시 사용할 수 있는 상태로 미리 준비해 두는 것
- 탈중앙화된 IT resource들의 집합에 네트워크를 통한 원격 접속 제공
Scaling
- 요구에 따라서 IT resource를 늘리거나 줄이는 것
(1) Horizontal Scaling
- 동일한 유형의 IT resource unit의 수를 조절
- scaling out : IT resource 개수를 늘림
- scaling in : IT resource 개수를 줄임

(2) Vertical Scaling
- IT resource unit을 사양이 크거나 낮은 다른 자원으로 대체하는 것
- scaling up : IT resoutre를 더 높은 사양으로 교체
- scaling down : IT resource를 더 낮은 사양으로 교체

(3) comparison of horizontal and vertical scaling

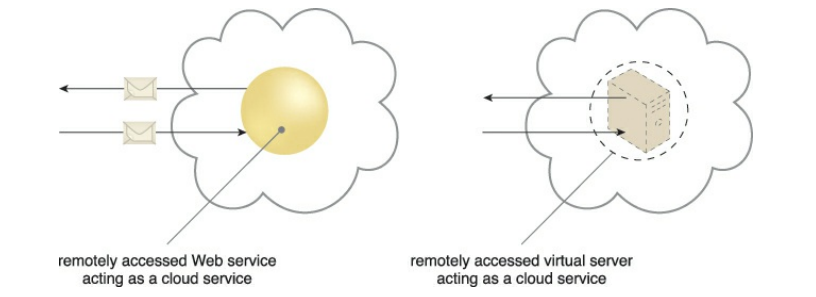
Cloud Service
- 원격으로 cloud를 통해서 접근 가능한 모든 IT Resource
- cloud 내 모든 IT 자원이 원격으로 접근할 수는 없고, 그 중에서 접근 가능한 것이 cloud service
3. Goals and Benefits
(1) Reduced Investments and Proportinal Costs - 투자, 비례 비용 절감
- 하드웨어, 소프트웨어 구매, 소유 비용 X → 선행 IT 투자 비용을 줄일 수 있다.
사용자 입장
- On-demand accss : 단기간을 기준으로 사용료를 지불하고, 필요없으면 자원을 방출 가능
- 사용할 수 있는 컴퓨팅 자원에 제약이 없어서 provisioning 할 필요가 없다. (미리 준비할 필요x)
- **세분화된 수준(fine-grained level)**에서 IT 자원을 추가하거나 제거 가능
- Abstraction of the infrastructure : 장치나 위치에 구애 받지 않고 application을 쉽게 옮길 수 있다.
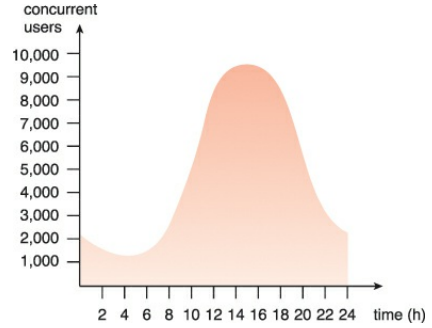
(2) Increase Scalability - 확장성 증가
- 필요할 때 언제든지 즉시, 동적으로 자원을 할당 가능 (On-demand)
- IT resource pool에서 자원 꺼내서 할당
- cloud 소비자는 자원을 확장하여 에측 불가능한 사용 요구를 대처할 수 있다.
- usage thresholid를 넘겨서 생기는 손실을 방지 (서비스 일시 중단 등)
(3) Increasd Availabilty and Reliability - 가용성, 신뢰도 증가
- IT 자원의 가용성을 높임 ⇒ 서비스 중단을 최소화, resilient IT resource
- IT 자원의 신로도 높임 ⇒ 장애를 줄임, failover support
4. Risks and Challenges
(1) Increased Security Vulnerabilities - 보안 취약성 증가

- 여러 기관의 trust boundary(신뢰 경계)가 cloud service에서 겹치게 된다.
- 이는, IT 자원을 원격으로 사용하기 위해서는 어쩔 수 없이 외부 cloud service까지 trust boundary를 확장해야 하기 때문.
- 여러 유저들이 접근하기 때문에 노출 가능
- Isolation이 안된다.
- trust boundary(신뢰 경계)끼리 중첩과 데이터의 노출 증가 ⇒ 악의적인 사용자가 공격 가능
(2) Reduced Operational Governance Control - 제어권 축소

- cloud 소비자는 보통 on-premise일 때 보다 낮은 수준의 관리 제어권을 제공받게 된다.
- cloud 제공 측에서 SLA(서비스 수준 협의서)에 맞지 않은 서비스를 제공할 수도 있기 때문에 소비자가 주시해야 한다.
- 소비자와 제공자 간 지리적 거리 → network로 통신 ⇒ unreliable network connection
- 만약 network에 장애가 생긴다면? → 성능 저하, 서비스 장애로 이어짐
(3) Limited Portability Between Cloud Providers - 제공자 간 제한된 이식성
- 아직 cloud 산업의 표준이 정해져 있지 않아 cloud 제공 업체에 따라서 그에 맞는 솔루션을 구축해야 함
- 다른 클라우드 제공업체로 옮기기 힘들다.
(4) Multi-Regional Compliance and Legal Issues - 다양한 지역 규제, 법적 문제
- cloud provider의 datacenter는 보통 접근하기 쉽고 편리한 위치에 설립한다.
- 이로 인해 해당 지역의 산업, 정부 규제에 영향을 받음
- data 접근과 사용에 관련해 여러 법적 issue 존재

(5) malicious attacks and failures of the infrastructure
- 디도스 - 2009년 구글 사례
- 정전 - 2012 아마존 사레
반응형
'Computer Science > Cloud computing' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Cloud computing] 7. Models (0) | 2022.12.04 |
|---|---|
| [Cloud computing] 6. Parallel & Distributed (0) | 2022.10.24 |
| [Cloud computing] 5. Virtualization (0) | 2022.10.14 |
| [Cloud computing] 3. Architecture (0) | 2022.10.13 |
| [Cloud computing] 2. Model (0) | 2022.10.12 |
![[Cloud computing] 1. Concepts](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FwCBMQ%2FbtrOoy9klAU%2FveK5KshZ320PwCcyYdTus0%2Fimg.png)